SIM vs eSIM Card: Key Differences Explained
- Categories Basic Telecom
- Date September 21, 2025
- Comments 0 comment
SIM vs eSIM Card: Key Differences Explained
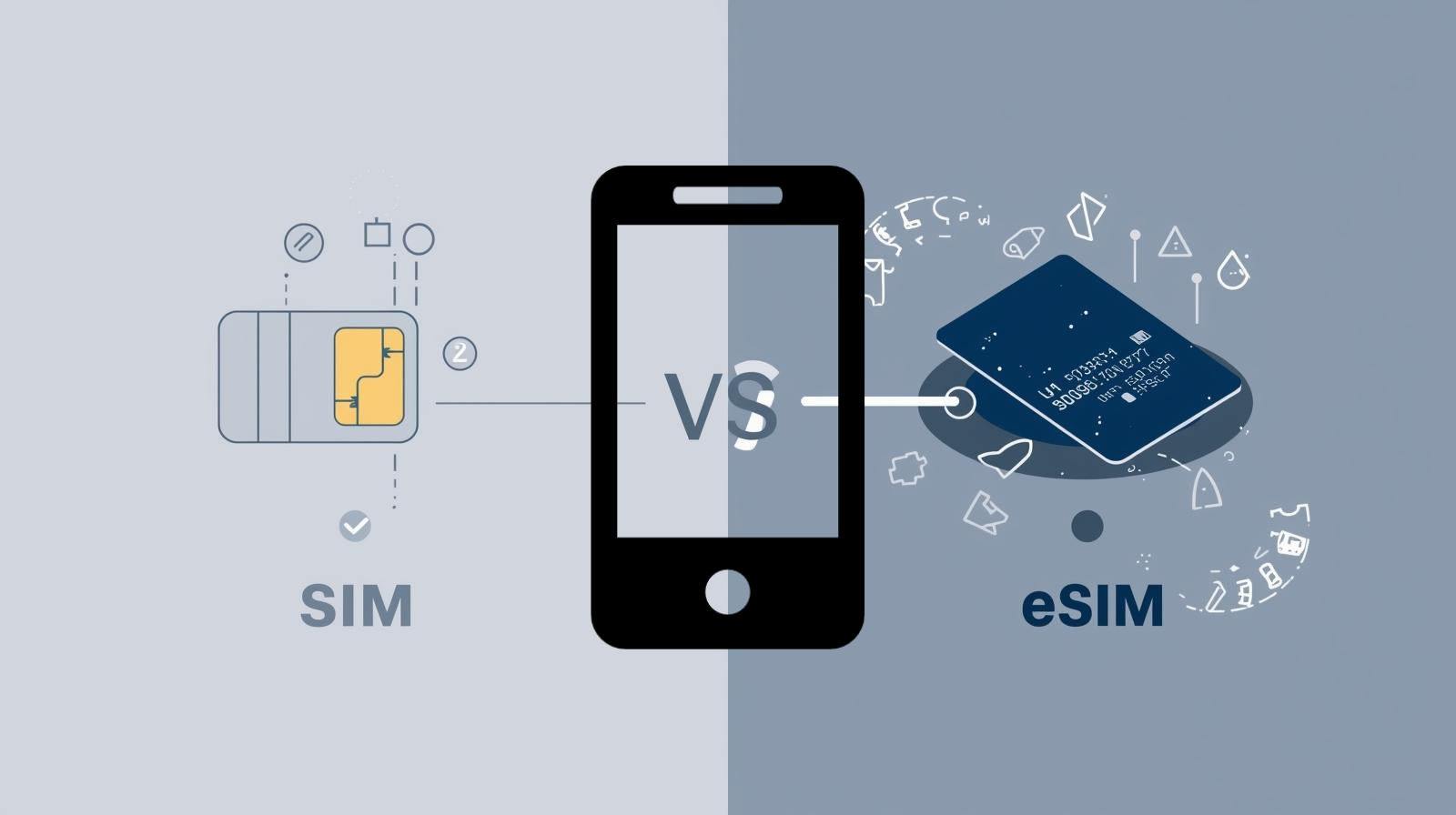
SIM vs eSIM card In today’s world, staying connected with network more important than ever. Whether it’s for work, socializing, or simply staying updated with the world around us, our mobile phones and Telecom are our lifelines. But have you ever stopped to think about the technology that keeps your phone connected to a network? It all comes down to the SIM card. When comparing SIM vs eSIM Card, it’s important to evaluate aspects like convenience, security, and compatibility.
But recently, a new player has emerged: the eSIM. If you’re wondering how it differs from the traditional SIM, and how they work, you’ve come to the right place. In this blog, we’ll dive into the details of SIM vs eSIM, helping you understand their features, differences, and how they impact your mobile experience. In this blog, we’ll break down everything you need to know about the SIM vs eSIM Card battle – from installation to benefits and drawbacks.
What is a SIM Card?
A SIM card (Subscriber Identity Module) is a small physical card that stores your unique identification information on your mobile device. It’s what connects your phone to your network carrier, enabling you to make calls, send messages, and use mobile data.
Traditionally, SIM cards have been inserted into a dedicated slot in your phone, and they store important data such as:
-
- Your phone number
-
- Your carrier’s network information
-
- Contacts (in some cases)
-
- Security keys for encrypted communication
There are several sizes of SIM cards – the Standard SIM, Micro SIM, and Nano SIM – but they all serve the same purpose: to identify and authenticate your device on your network.
What is an eSIM?
An eSIM (embedded SIM) is a newer technology that replaces the need for a physical SIM card. Instead of inserting a physical card into your device, the eSIM is built directly into your phone’s motherboard. This small chip acts just like a SIM card, but it’s embedded in the device, allowing you to activate a cellular plan without needing a physical card.
Key Features of eSIM:
-
- Embedded Chip: The eSIM is soldered into your device and cannot be removed.
-
- Remote Provisioning: eSIMs can be activated and programmed over-the-air (OTA), meaning you can switch carriers or plans without needing a new SIM card.
- Multiple Profiles: eSIMs can store multiple carrier profiles, making it easier to switch between networks or even use different networks simultaneously (like having both a personal and work number on the same device).
How Do They Work?
Traditional SIM Card
When you insert a physical SIM card into your phone, the card essentially “tells” the device which network to connect to. The carrier you’ve chosen provides the SIM card, which contains your unique identification and security information. Every time you connect to the network, the SIM authenticates your phone, ensuring that your device is authorized to use that network.
The SIM is tied to a specific carrier, and if you wish to change providers, you’ll need to physically replace your SIM card with one from the new carrier. This can sometimes be a hassle, especially if you’re traveling internationally and need to swap SIMs frequently.
eSIM Technology
With an eSIM, the process becomes much more flexible. The eSIM is a chip embedded in your device, and it can hold multiple carrier profiles. Instead of physically swapping cards, you can remotely download a new carrier profile to your phone.
When you switch carriers or activate a new plan, you no longer need to go to a store or wait for a physical SIM card to arrive in the mail. Instead, you can simply scan a QR code or enter details provided by your carrier, and the new carrier profile will be downloaded and activated on your phone.
This means:
-
- No more physically swapping SIM cards.
-
- The ability to have multiple carriers or plans on a single device.
-
- It’s easier to switch to international carriers when traveling, without worrying about swapping SIMs.
Key Differences: SIM vs eSIM
| Feature | SIM Card | eSIM |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Form | Physical card that needs to be inserted | Embedded chip in the device |
| Switching Carriers | Requires a new physical SIM card | Can switch carriers remotely over-the-air (OTA) |
| Device Compatibility | Must have a SIM slot | Available on newer devices (e.g., iPhone, Google Pixel) |
| Storage | Stores data for one carrier at a time | Can store multiple carrier profiles |
| Convenience | Requires physical swapping for changing networks | Easy to change networks and plans remotely |
| Space | Takes up physical space in your device | Saves space in your device, ideal for compact designs |
Advantages of eSIM over SIM
-
- No Need for Physical Cards
With eSIM, there’s no need to physically swap SIM cards when you change carriers or plans. You simply download the new profile over the air, which is more convenient and faster.
- No Need for Physical Cards
-
- Multiple Profiles on One Device
One of the best features of eSIM is the ability to have multiple profiles on a single device. You can store several carrier profiles and easily switch between them. This is great for travelers who want to use a local carrier while abroad or those who need separate personal and work numbers.
- Multiple Profiles on One Device
-
- Compact Devices
Because the eSIM is embedded into the device, it saves physical space that would otherwise be taken up by a traditional SIM card slot. This can lead to slimmer and more compact designs, which is great for manufacturers aiming to make more streamlined devices.
- Compact Devices
-
- Better for Dual SIM
If you want to use two phone numbers on one device (for example, a personal and a business number), eSIM makes it easier. Many modern smartphones allow for dual SIM functionality, with one physical SIM card and one eSIM, offering more flexibility without needing two physical slots.
- Better for Dual SIM
Is eSIM Available Everywhere?
While eSIM technology is growing in popularity, it’s still not universally available. Currently, most newer smartphones, like the iPhone 17 and later models, Google Pixel 3 and newer, and some Samsung Galaxy devices, support eSIM. However, not all carriers worldwide support eSIM, so it’s important to check with your network provider to see if they offer eSIM compatibility.
Moreover, eSIM technology is especially useful for those who travel internationally. Instead of dealing with the hassle of swapping SIM cards every time you enter a new country, you can easily download a local carrier profile via eSIM, making global roaming more seamless and less expensive.
Airtel and Jio have Most number of eSIM user in India
SIM vs eSIM Card: Key Differences Explained
You may also like

2G vs 3G vs 4G vs 5G: Key Differences Explained
What is Spectrum in Telecom?